WMI Connection Diagnostics for Collecting Remote Inventory Information
Method 1. Checking the connection via WMI using the wbemtest utility
-
Open the wbemtest utility: Start - Run - wbemtest (or press the key combination
Windows+R - wbemtest).
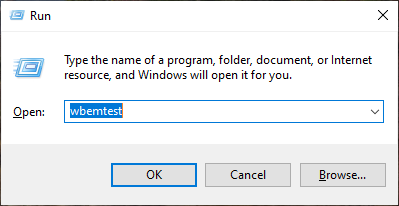
- Click Connect.
If you are checking the connection for the PC on which you launched the utility, you do not need to enter anything, click
Connect.
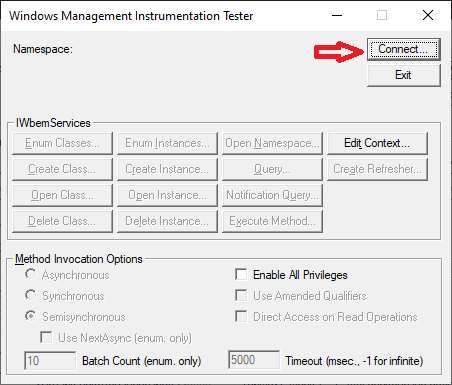
-
In the Namespace field, before the standard namespace, enter through
\\Computer (for example,
\\Comp1\root\cimv2, where Comp1 is the Name of the PC to which we are
connecting).
-
In the User field, enter the Name of the user who has access to
this PC.
-
In the Password field, enter the password for the user entered above.
-
Click Connect.
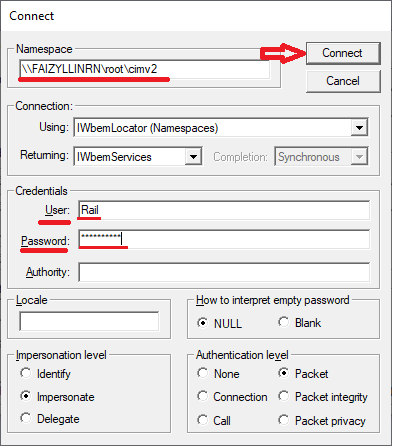
-
Click the Request button.
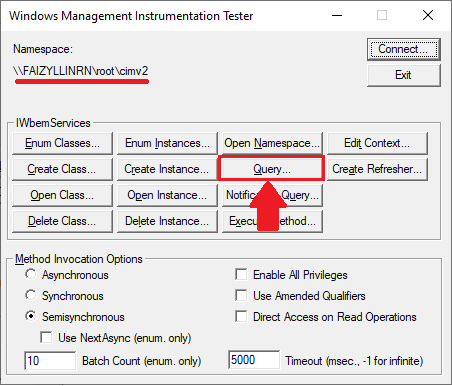
-
Enter a query to get the operating system name and click the Apply button:
SELECT Name FROM Win32_OperatingSystem
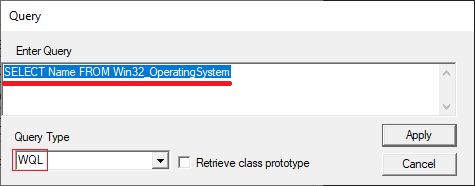
To obtain information, WMI uses the WQL query language.
Query syntax in WQL is similar to SQL:
SELECT (what get) FROM (where_from).
The main difference is that instead of SCHEMA name the WMI class is used.
-
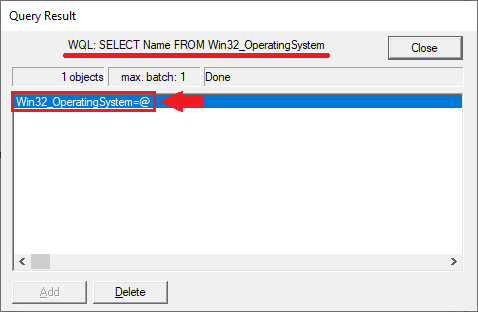
Double-click on Win32_OperatingSystem=@.
-
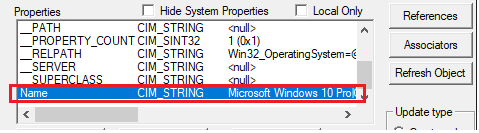
In the Properties window, find and view the value of the Name property.
Method 2. Checking the WMI connection in PowerShell
-
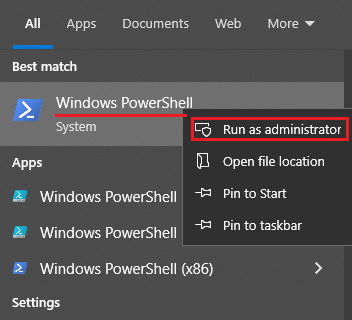
Open PowerShell as administrator: click START (or magnifying glass icon in
Windows 10/11) - in the search
line, enter PowerShell, right-click on Windows
PowerShell, - Run as administrator.
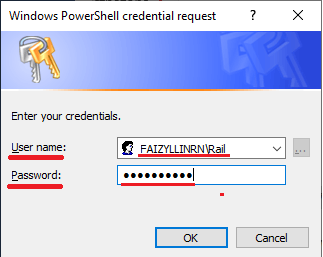
- In the PowerShell window, enter the query:
Get-WmiObject -Query "SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem" -ComputerName IEWIN7 -Credential
IEWIN7\Admin | ft
-Property Name, BuildNumber
Where -Query "SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem" is the query itself (get all the information about the
OS),
IEWIN7 is the name of the PC to which we are connecting, IEWIN7\Admin is the user who has access to the PC (preferably an administrator), -Credential is a query using the built-in Windows account manager, ft =
Format-Table, -Property Name, BuildNumber is to display only the OS Name
and Build Number.
- Enter the password for the specified user.
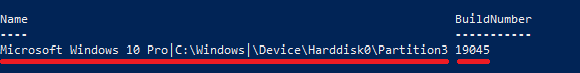
- After entering the password, we will receive the requested information in the form of a table
Diagnosing WMI connection problems
- If you are unable to connect, make sure that the Username and
password you entered are correct and try connecting again.
- If you are sure that you entered the connection data correctly, start the following services and try
connecting again:
- Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Locator Service.
- Remote Access Automatic Connection Manager (RasAuto) Service.
- If the Username and password are correct and all necessary services are running,
check the Firewall settings. Typical firewall settings can be viewed on our website Configuring WMI access remotely via Group Policies starting with point 7









