What is Syslog: Things You Need To Consider

In today’s complex IT environments, effective logging and monitoring are critical for maintaining system integrity and security. Syslog, a foundational tool in centralized logging, enables organizations to log system messages and events across devices and applications. By transmitting log messages to a centralized syslog server, Syslog simplifies log management, allowing organizations to store, analyze, and act on important data efficiently.
What is Syslog?
Syslog is a standardized protocol for collecting and managing system messages in networked environments. It enables log data transmission from various devices and applications to a centralized server for efficient management and analysis.
History of Syslog

Syslog was developed in the 1980s by Eric Allman as part of the Sendmail project, which was a widely used mail transfer agent in Unix systems. It quickly became a de facto standard for centralized logging due to its simplicity and effectiveness in capturing log messages from various sources.
The protocol was not formally standardized until 2001 when the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) published RFC 3164, known as “BSD syslog.” This document outlined the basic structure and transport methods for syslog messages. In 2009, RFC 5424 superseded RFC 3164, introducing enhancements such as ISO-8601 timestamps, structured data fields, and support for UTF-8 encoding.
Initially, syslog messages were transmitted using User Datagram Protocol (UDP), which is fast but does not guarantee delivery. Over time, support for Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Reliable Event Logging Protocol (RELP) was added to ensure more reliable message delivery. Modern implementations also support TLS encryption for secure transmission of log data.





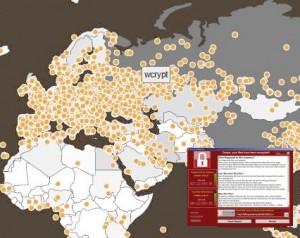 When you hear about the “Wanna Cry” virus infections in various companies on news, it is becoming vital to know and to check whether your company computers are vulnerable to this virus or not. Our
When you hear about the “Wanna Cry” virus infections in various companies on news, it is becoming vital to know and to check whether your company computers are vulnerable to this virus or not. Our