![]() 1.
Launch the application.
1.
Launch the application.
If you are running the application for the first time, you will see the application's main window and the Network Scanning Wizard window.
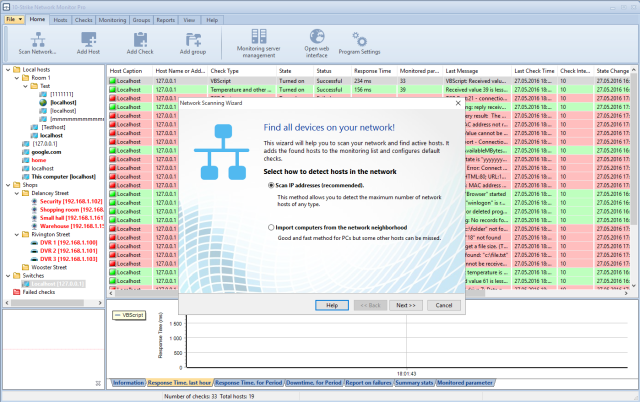
By following the instructions of the Wizard, you can quickly and easily find hosts on the network and add them to the monitoring list with preconfigured default checks.
The Wizard uses two methods for searching network devices:
Scanning IP range
This method allows you to spot the maximum number of devices. It features the following advantages:
- High scanning speed (up to 16 addresses/sec.[1])
- Recognition of diverse hardware types: printers (local and network), switches, hubs, servers, database servers, routers, WiFi access points, etc.
- Combination of several efficient network hardware search methods (ICMP ping, scanning a series of TCP ports, ARP requests).
- Retrieving data from hardware via SNMP (switches, printers, WiFi, etc.)
- Automatically building a network map by drafting over data received from switches .
- Automatic retrieving of additional information on found hosts (IP and MAC addresses, NIC manufacturer, DNS name, OS type, connected printers, descriptions.)
- Scanning several IP ranges at once.
- When found devices are placed on the map, they are automatically scheduled for specific automatic checks.
If you network is rather large, this scanning method is recommended.
[1]How to configure optimal scanning settings
The perfect choice of search parameters depends on your network configuration, availability and functioning of the necessary protocols. In particular, to detect hosts in a local area network with bandwidth of 100 Mbps and higher, sufficient will be two ping packets and a 100-500 ms response. In the case with TCP ports, it is worth noticing that the greater number of ports you specify on the list, the longer the application will search for hosts in the network. The best way to go around this is to set 2-3 most common ports through which the application can find Windows stations and servers; those include 139, 21 and 80th (NetBIOS, FTP, HTTP).Searching for network printers is a different story. This procedure takes quite a bit of time, and therefore it should not be run if you are SURE that there are no such printers in your network. Otherwise, you would have to wait for the completion of that procedure. The completion will be indicated by the appearance of the network scanning progress bar in the network scanning wizard window. The reason why the procedure is so slow is because it searches for network printers BEFORE launching the primary scanning procedure (which is performed with a large number of threads running simultaneously, unlike with searching for printers).
This is also true for obtaining additional information on hosts through NetBIOS . If the NetBIOS protocol is disabled in your network, no such information can be retrieved, and the application will spend quite a bit of time on that attempt (hence the feeling that the application is “frozen”). Searching for network switches is done in the multithreaded mode. However, if you specify a large number of possible community string values, that will also slow down the scanning process. Hence, if you have set the scanning parameters, and the application is scanning too slow or, even worse, completely "frozen" – go ahead and disable some of those parameters (first, disable network printer search and then disable obtaining additional information through NetBIOS) and try launching the scanning procedure again.
Importing from Network Neighborhood.
This method works somewhat faster than the other one; however, not all devices are guaranteed to be found. Moreover, using this method the program will not be able to build the network map automatically. Still, it will automatically place found computers to groups, depending on workgroups and domain names the computers belong to.
You can find more details on the scanning process in the topic Creating the list of network hosts.
If the Wizard was unable to find all hosts, you can add the missing ones to the monitoring list manually. Besides, you can use the application's tools to split the found hosts into groups by creating those and then dragging the hosts into them with the mouse.
![]() 2. Add custom checks to the found hosts.
2. Add custom checks to the found hosts.
To each host found by the network scanning wizard, the application automatically assigns a specific check with the type that depends on the method used for finding the host (ICMP ping, TCP port, ARP ping). You can keep those checks, having changed the default settings and added additional checks as necessary. All changes are saved to the .ini file and take effect immediately.
![]() 3. Use the context, main menu and toolbar for accessing the application's functions.
3. Use the context, main menu and toolbar for accessing the application's functions.
All functions of the application are available through the context menu, toolbar, main menu and will be described further on.